
The ENDOCANNABINOID System
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex cell-signaling system that plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis within the body. Discovered in the late 20th century, the ECS is involved in regulating a wide range of physiological processes, from pain and mood to appetite and immune response. Understanding how the ECS works, what happens when it is out of balance, and how cannabis interacts with it can provide valuable insights into its importance for health and wellness.
Endocannabinoids
These are naturally occurring compounds in the body, including anandamide and 2-AG, that bind to cannabinoid receptors.
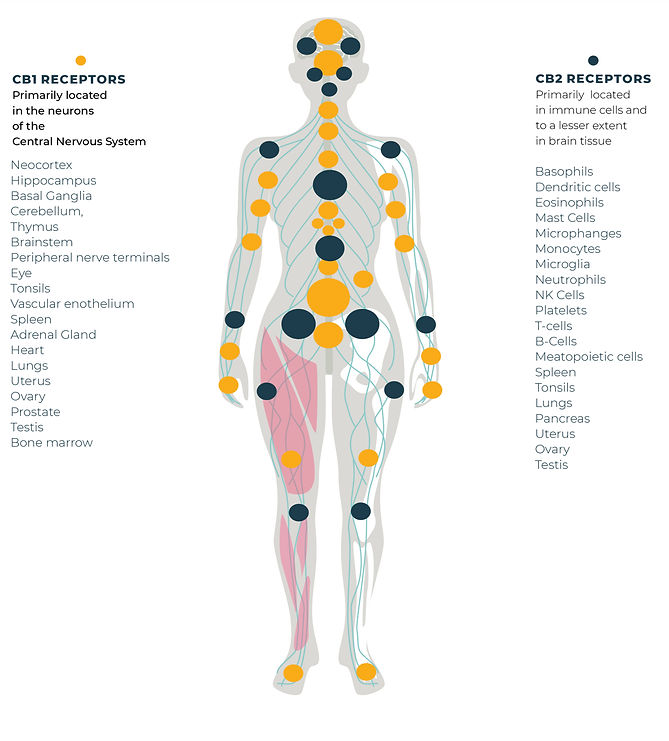
Cannabinoid Receptors
These are proteins found on the surface of cells. The two primary receptors are CB1 and CB2.3.
Enzymes
These are responsible for synthesizing and breaking down endocannabinoids after they have carried out their function.
The ECS regulates a variety of physiological processes, including
-
Pain Modulates pain perception and reduces inflammation.
-
Mood Influences mood regulation and stress response.
-
Appetite Controls hunger and metabolism.
-
Immune Function Modulates immune system activity and inflammation.
-
Memory Affects memory formation and retrieval.Sleep Regulates sleep patterns and circadian rhythms.
Heading 5


Discovery of the ECS
The ECS was discovered in the early 1990s through groundbreaking research by scientists exploring the effects of cannabis on the human body. In 1988, Dr. Allyn Howlett and her team at St. Louis University identified the first cannabinoid receptor, CB1, in the brain. This discovery was followed by the identification of a second receptor, CB2, found primarily in the immune system and peripheral tissues.In 1992, Dr. Lumír Hanuš and Dr. William Devane at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem identified the first endogenous cannabinoid, anandamide. This discovery revealed that the body produces its own cannabinoids, which interact with the ECS. A second endogenous cannabinoid, 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), was discovered shortly thereafter, further expanding our understanding of the ECS. Functions and RegulationThe ECS consists of three main components:
Imbalance in the ECS
When the ECS is out of balance, it can lead to various health issues. An imbalance in the ECS is thought to be linked to conditions such as:
Chronic Pain Insufficient endocannabinoid signaling can result in increased pain sensitivity.
Anxiety and Depression Dysregulation of the ECS may contribute to mood disorders.
Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases Overactive immune responses can be moderated by the ECS.
Metabolic Issues ECS imbalances can affect metabolism and appetite, potentially leading to obesity or eating disorders.
Neurodegenerative Diseases Proper ECS functioning is crucial for protecting neurons and maintaining brain health.
Interaction with Cannabis
Cannabis contains phytocannabinoids, such as THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol), which interact with the ECS to produce their effects.
THC
The primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, THC binds directly to CB1 receptors in the brain, producing euphoria and altered sensory perception. THC also interacts with CB2 receptors, contributing to its anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
CBD
Unlike THC, CBD does not bind directly to CB1 or CB2 receptors. Instead, it modulates the receptors’ activity and influences the body’s production of endocannabinoids. CBD is known for its anti-anxiety, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective properties, and it can mitigate some of the psychoactive effects of THC.
Therapeutic Implications
The interaction between cannabis and the ECS has significant therapeutic implications. By targeting the ECS, cannabinoids from cannabis can help restore balance and alleviate symptoms in various conditions, such as:
Chronic Pain Cannabis-derived cannabinoids can reduce pain and inflammation, offering an alternative to traditional pain medications.
Epilepsy CBD has been shown to reduce the frequency and severity of seizures in certain forms of epilepsy.
Anxiety and PTSD CBD’s anxiolytic effects can help manage anxiety and post-traumatic stress disorder symptoms.
Autoimmune Diseases By modulating immune responses, cannabinoids can reduce inflammation and improve symptoms in autoimmune conditions like multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis.
The endocannabinoid system is a critical regulatory network in the human body, involved in maintaining homeostasis across various physiological processes. Discovered in the 1990s, the ECS has since become a focal point for understanding how cannabinoids, both endogenous and from cannabis, influence health and disease. When the ECS is out of balance, it can lead to a range of health issues, but cannabinoids from cannabis offer a promising avenue for restoring balance and improving well-being. As research continues to expand our knowledge of the ECS, its role in health and medicine will undoubtedly become even more significant.
Got more Questions?
OUI are here to help. Connect with an OMEGA — with her by your side, you're not just finding products — you're unlocking YOUR health and well-being journey through the transformative power of cannabis.

